With our 2023B release, we added new variables on health insurance coverage. These variables will prove invaluable for urgent care site selection, insurance marketing and more. We have not only the various types of insurance you can have—employer-based, direct purchase, Medicare, TRICARE, VA, or none—but also the combination of different kinds of insurance and breakdowns by age group. As a preview, we wanted to show you some maps and give additional insights into this new data.
First, let’s breakdown some nationwide statistics. Employer-based only insurance accounts for the highest coverage levels at 41.6%, followed by TRICARE/Military Coverage only at 12.5%, Medicare only at 7% and no coverage at 6.7%. Nearly 1 in 5 people have multiple types of insurance, with the combination of Medicare and employee-based insurance being the most common after other coverage combinations, likely a mix of private and public options.
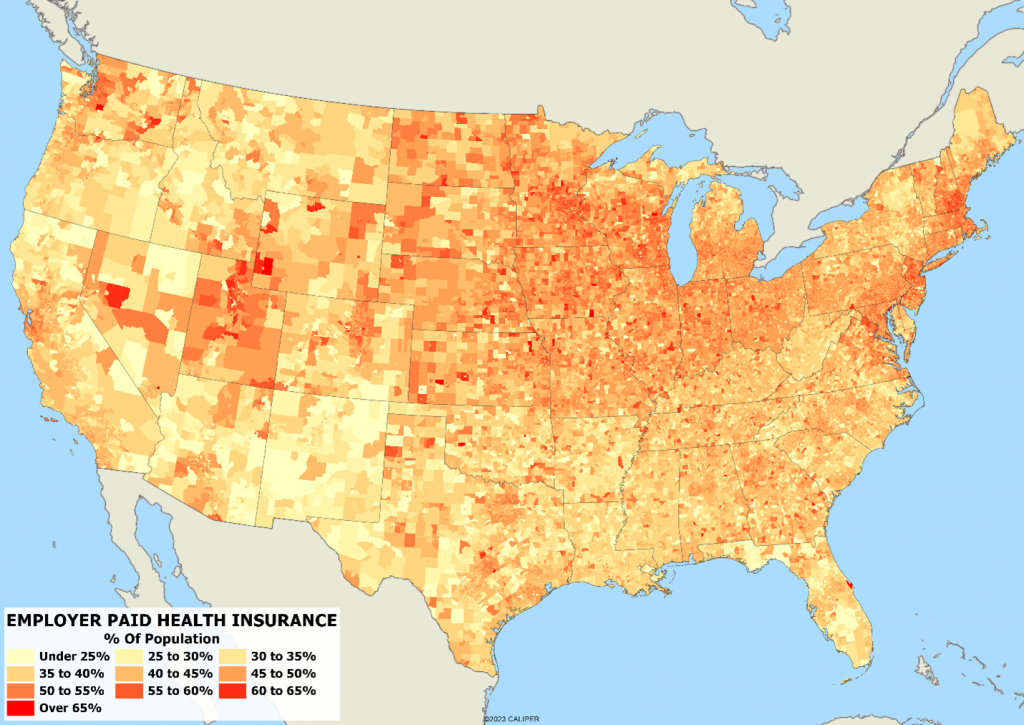
The first map is of employer-based health coverage. This is typically larger firms and companies, located mostly in the major metropolitan areas across the country. The highest percentage of coverage is in Utah, where over 55% of the policies are employer-based. Rounding out the top 5 are New Hampshire, Minnesota, New Jersey, and Wisconsin. New Mexico, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Arkansas are the bottom 5 states in terms of employer-based health coverage.
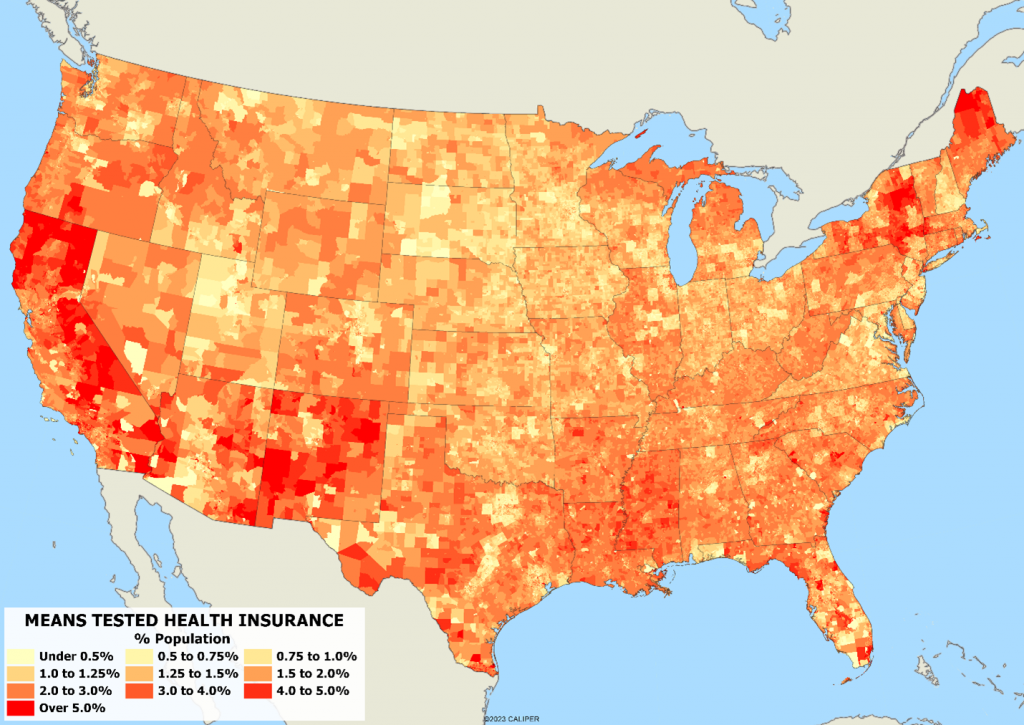
Means tested insurance, meaning health insurance provided by the state to those who qualify financially, has a definite state pattern based on state policies. States that prioritize healthcare benefits to residents are clearly shown on the map below. The top states giving Means tested insurance are New York, Mississippi, California, Louisiana, and New Mexico. Though not a state, the District of Columbia ties for 5th place. The bottom five in providing means tested insurance are Utah, South Dakota, New Hampshire, Nebraska, and Virginia, Minnesota, and North Dakota all tied with just 1% of the state population receiving these benefits. As you can see on the map below, rural California, New Mexico, New York, and Maine have high rates of means tested insurance.
Finally, a map of areas with no health insurance at all, where again, the state patterns emerge. This could be in part an artifact of the ACS stratified spatial sampling model, but it clearly also reflects state level insurance practices and the attitudes of many in the southern states about health care insurance and government benefits. The top 5 states with populations without health insurance are Texas, Alaska, Oklahoma, Georgia, and Wyoming, with Massachusetts, Vermont, Connecticut, Minnesota and Rhode Island having the least number of uninsured citizens.



Recent Comments