Most of the major financial institutions have established separate private branches, or at least special investment teams, for their large clients. The SEC limits many transactions to high net worth individuals. Two categories are generally used –
- Accredited investors are those who have individual income over $200,000 for the last two years ($300,000 for a couple) and have a net worth, excluding equity in a principal residence, of over $1,000,000
- Qualified investors must have a net worth exceeding $5,000,000, again excluding equity in a principal residence.
As part of our 2024B update, we are expanding our synthetic household-based Household Finances database to include two household distributions that provide detail on the distribution of net worth – both overall and net of primary residence. The map below shows the percentage of households with a net worth exceeding $1,000,000 exclusive of primary residence equity.
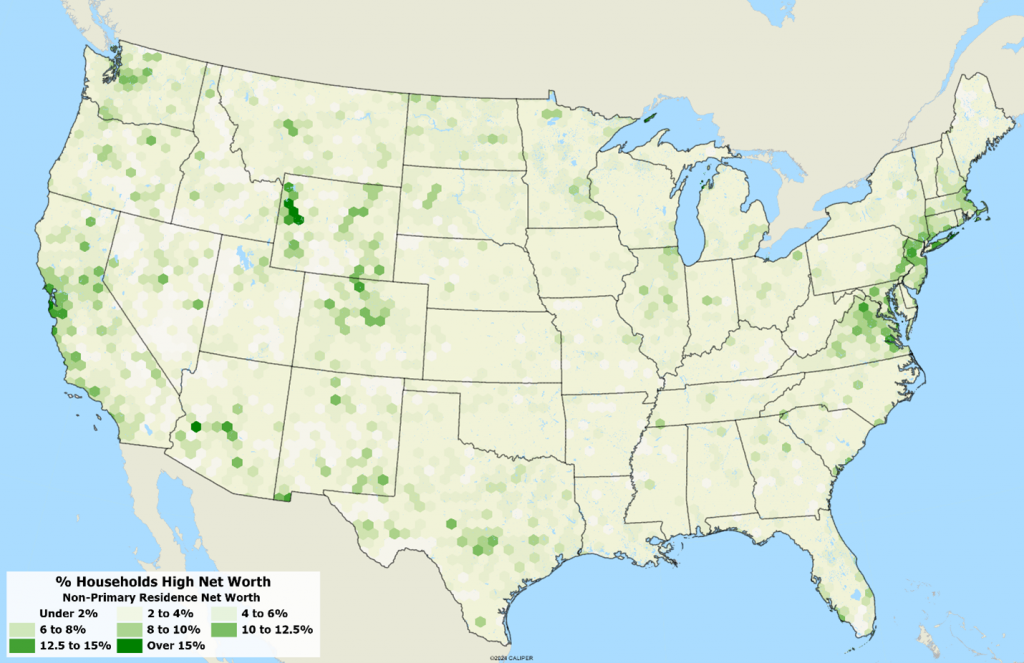
Nationwide, the percentage of households by net worth – total and excluding primary residence – who have net worth over $1,000,000 is X and Y percent respectively.
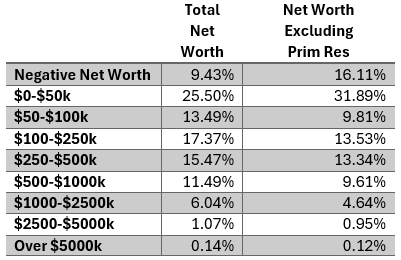
Roughly 5.7% of households nationwide meet the asset requirements to be accredited, and a small fraction of those meet the requirements of qualified investors – although both categories allow non-individual entities to be considered (such as partnerships and corporations).
On the flip side, households with negative net worth account for 9.43% with residential equity included, but over 16% when excluded. Negative net worth households predominate in low-income areas, especially in rural areas:
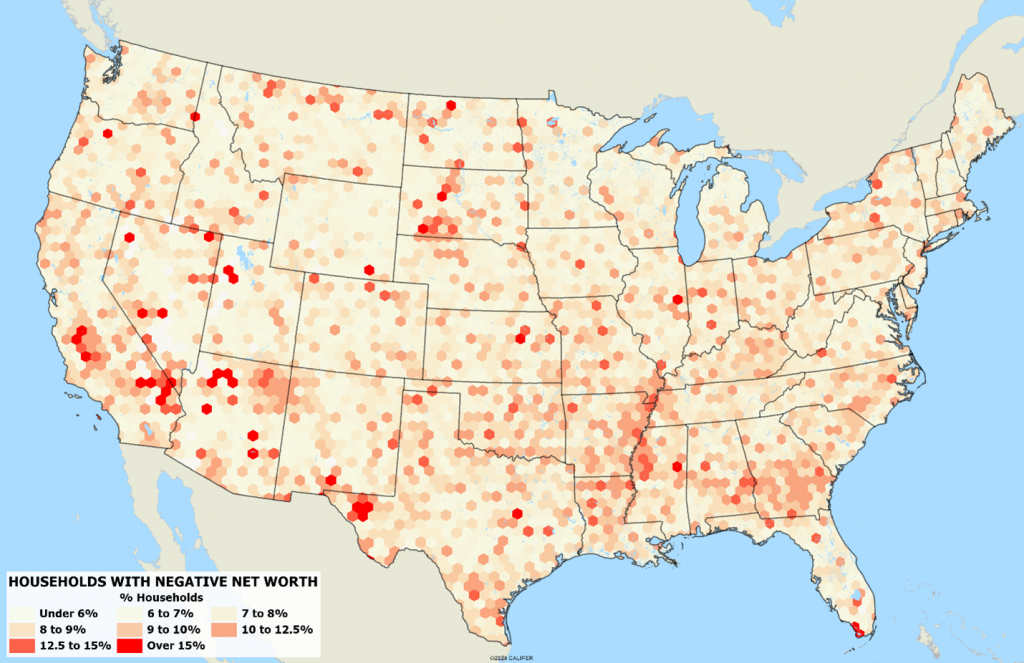
The updated household finance database is native to the census block level, and available beginning with the November 2024B release for all standard geographic areas including block group and hexagon layers.
